
The benefits of fingerprint identification
Fingerprint identification is the most widely known and oldest form of biometric signature, with a history that spans more than a century, originating in forensic applications. Today, it’s widely used for access to a range of devices, from access points to smartphones. The technology comes in different formats, sizes, and shapes, using different types of sensor points, so it can be customised to suit any environment and application.
Fingerprint Identification
While there are a number of methods for capturing fingerprint images, the two most commonly used are optical sensors and capacitive scanners, as they are suited to a wide range of environments and applications.
Optical sensing:
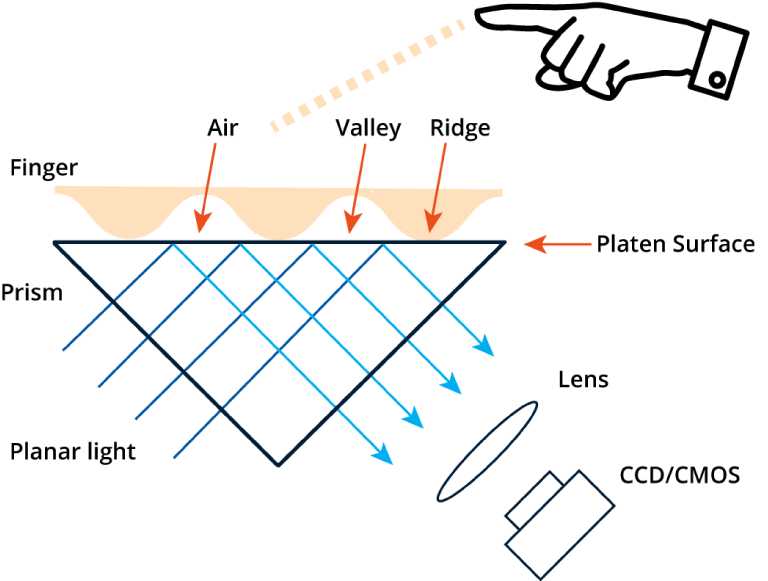
This method uses an image sensor to capture a picture of the fingertip surface and works in a similar manner to a digital camera. Just below the scanning surface, there is an array of minuscule capacitors that act as a collection point for fingertip details. When the user touches the scanning surface, the charge changes just below the friction ridges on the fingertip, allowing the device to record the unique pattern of ridges and valleys, which is then run through a fingertip recognition algorithm.
In addition, multispectral imaging (MSI) significantly reduces the chances of spoof attacks by capturing the features of the user’s fingertip tissue below the skin surface. These sub-surface features provide the second tollgate for the system to check and match the pattern on the fingertip surface. MSI sensors can collect useable images in adverse conditions, such as when the skin surface is worn. They can also distinguish between a living digit and soft materials, making them less vulnerable to sensor attacks.
Capacitive scanning:
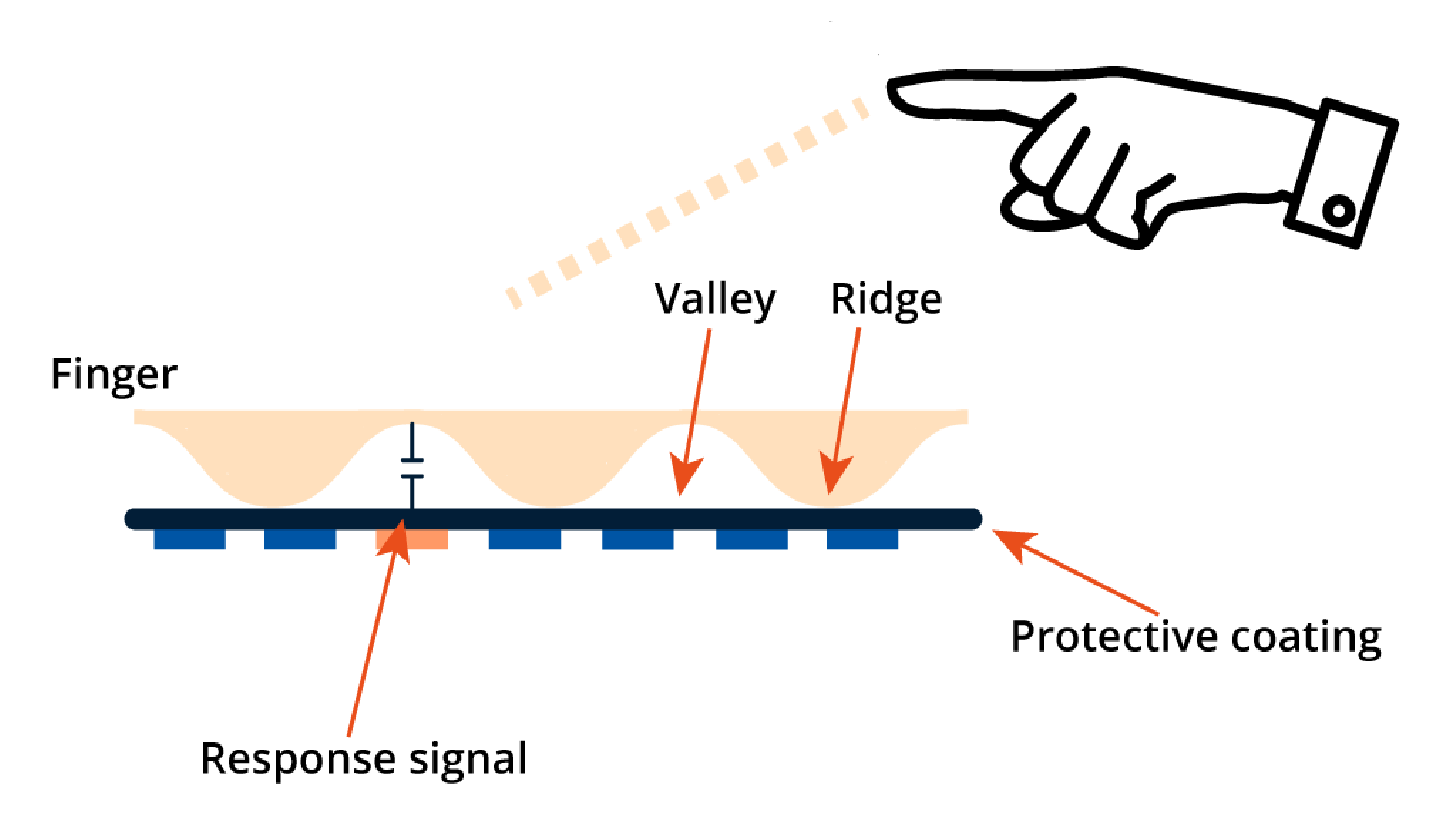
Like the optical method, capacitive scanners also use tiny capacitors under the scanning surface, however, they do not capture the fingerprint optically, making them typically more secure. The friction ridges and valleys are tracked by an op-amp integrator circuit, which can then be recorded by an analogue to digital converter. Capacitive scanners are typically used for high-security applications.
Business applications
Fingerprint identification is suited to a wide range of environments and applications. The most common business uses are to access high value assets and into secured environments.
Industry solutions
Fingerprint recognition systems have been utilised for many years across a variety of industry sectors. Recent technological advances, such as multispectral imaging, have increased both the accuracy and security of this modality.

Childcare
Services
Benefits summary
Widely accepted
Fingerprint readers are used widely today, from personal device access to high-security industry applications, and most users are familiar and comfortable with the technology, meaning they typically require minimal end user training.
Flexible
In most applications, fingerprint readers offer a flexible solution. Their small form factor enables them to be installed easily, even when space is at a premium, and the wide variety of available units means there is a solution to address even the most specific of requirements.
Cost -effective
With such a wide range of devices supporting fingerprint technology, it is widely-recognised as one of the most cost-effective solutions when you need certainty of identity.
Let’s start a conversation
Deciding which biometric modality to use can be confusing. But remember, the technology is only a small part of a successful solution. We focus on your business challenges first, to determine what solution will work best for your environment. In fact, that’s why Argus exists. We’d love to help you put identity at the centre of your organisation, so let’s connect!


